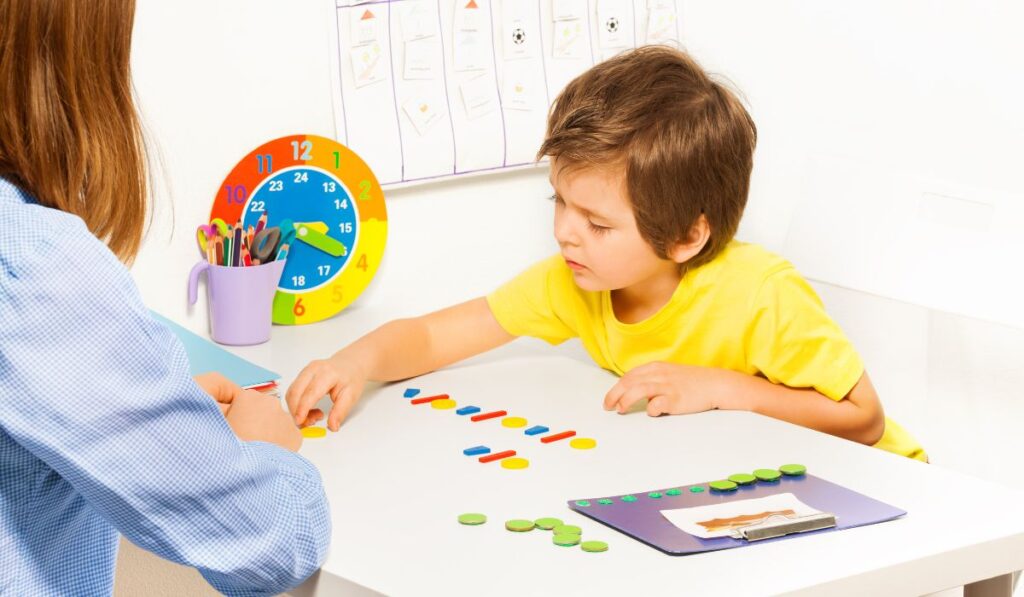
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has become one of the most effective, evidence-based treatments for children with autism. Rooted in the principles of behavior science, ABA therapy is tailored to meet the individual needs of each child. It focuses on teaching meaningful skills, reducing challenging behaviors, and promoting independence.
For many families, ABA therapy is more than just a clinical intervention—it’s a life-changing journey. In this article, we’ll explore how ABA therapy transforms the lives of children with autism and empowers them to reach their fullest potential.
Understanding Autism and ABA Therapy
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. Children with autism may struggle with verbal communication, making eye contact, managing their emotions, or understanding social cues. While each child on the spectrum is unique, early intervention is universally recognized as critical to long-term success.
ABA therapy is grounded in the science of learning and behavior. It involves analyzing a child’s behavior to determine what drives it, then using structured techniques to teach positive behaviors and reduce those that interfere with learning or daily life. ABA therapists break down complex skills into smaller, teachable components—using reinforcement and repetition to help children learn in a consistent, encouraging environment.
Personalized Learning Plans for Meaningful Progress
One of the most impactful aspects of ABA therapy is its individualized approach. No two children are alike, and ABA programs are custom-designed based on detailed assessments of each child’s strengths, needs, preferences, and goals.
From learning how to brush teeth independently to initiating a conversation with a peer, every skill targeted in therapy is chosen with intention. These personalized plans make learning meaningful and help children build practical, everyday skills that enhance their quality of life.
For example:
-
A nonverbal child may learn to use picture exchange communication (PECS) or speech-generating devices to express their needs.
-
A child with repetitive behaviors may be taught coping strategies to manage anxiety in new situations.
-
A child struggling with social skills may practice turn-taking, sharing, and reading facial expressions.
Building Communication Skills
Communication is often a major hurdle for children with autism. Whether verbal or nonverbal, many children have difficulty expressing themselves in ways others can understand. ABA therapy focuses extensively on enhancing communication—both verbal and alternative forms.
By using reinforcement and structured teaching, children can learn:
-
To request items or activities (manding)
-
To label objects and describe actions (tacting)
-
To engage in conversations and respond to questions
-
To understand and follow directions
Improved communication reduces frustration for both the child and the family, and it opens the door to more positive social interactions.
Promoting Social Skills and Emotional Regulation
Social challenges are a hallmark of autism. Many children struggle to engage in typical peer interactions or understand the unwritten rules of social behavior. ABA therapy addresses this by teaching social skills in ways that are natural, interactive, and functional.
Children practice these skills through role-playing, group settings, and real-world scenarios. Therapists may teach a child how to:
-
Maintain appropriate personal space
-
Interpret facial expressions and emotions
-
Initiate and maintain conversations
-
Play cooperatively with peers
In addition, emotional regulation is a key focus. Children learn how to identify their feelings, use calming techniques, and make choices that lead to positive outcomes—all of which contribute to healthier relationships and better self-control.
Encouraging Independence and Daily Living Skills
One of the long-term goals of ABA therapy is to help children with autism become as independent as possible. From self-care to academic tasks, ABA breaks down complex routines into manageable steps.
Examples of daily living skills addressed in therapy include:
-
Dressing and hygiene
-
Toilet training
-
Meal preparation
-
Time management
-
Cleaning and organizing personal space
By reinforcing each successful step, ABA therapy helps children gain confidence in their abilities and prepares them for greater independence at home, in school, and in the community.
Managing Challenging Behaviors
Challenging behaviors such as aggression, self-injury, tantrums, or elopement (wandering away) can be significant obstacles for children with autism and their families. ABA therapy is especially effective in addressing these behaviors.
Therapists conduct Functional Behavior Assessments (FBAs) to determine the root causes of behaviors—whether it’s a need for attention, escape from a task, or access to a preferred item. Once the function is identified, therapists create behavior intervention plans (BIPs) that teach more appropriate, alternative behaviors.
For example:
-
A child who hits to avoid a task may be taught to request a break instead.
-
A child who screams for attention may be taught to say “look at me” or tap someone gently.
Over time, these strategies not only reduce problem behaviors but also improve the child’s ability to function in different settings.
Support Beyond the Therapy Room: Family Involvement
Another key factor in the success of ABA therapy is active family involvement. Parents and caregivers are encouraged to participate in therapy sessions, learn techniques, and carry them over into everyday life.
This consistency across environments accelerates learning and ensures skills are reinforced outside the clinical setting. Many ABA programs also offer parent training and support, empowering families to feel confident and capable in guiding their child’s development.
Real-Life Transformations
Across the globe, thousands of families have experienced the positive impact of ABA therapy. Stories of children who once had limited verbal communication now speaking in full sentences, or children who couldn’t tolerate change now thriving in school routines, are a testament to the power of ABA.
While progress looks different for every child, the common thread is growth—growth in skills, confidence, and opportunities.
Looking for ABA home therapy in North Carolina? We provide personalized, in-home services to help children with autism learn, grow, and thrive.
Final Thoughts
ABA therapy is more than a clinical approach—it’s a transformative tool that helps children with autism navigate the world with greater ease and independence. By focusing on communication, social skills, daily living, and behavior management, ABA lays a foundation for lifelong success.
Families who choose ABA therapy are investing in their child’s potential. With consistent support, expert guidance, and an individualized plan, children with autism can make incredible strides—and ABA helps make that journey possible.
- How ABA Therapy Transforms the Lives of Children with Autism
- Discover how ABA therapy helps children with autism develop communication, social, and life skills for greater independence and success.
- #aba therapy
Related posts:
 How Laparoscopic Simulators Improve Precision & Reduce Surgical Errors
How Laparoscopic Simulators Improve Precision & Reduce Surgical Errors
 Exploring the Best Non – Surgical Treatments for Fibroids in Gurgaon
Exploring the Best Non – Surgical Treatments for Fibroids in Gurgaon
 Comprendiendo el Precio de Trasplante de Cabello y Sus Factores
Comprendiendo el Precio de Trasplante de Cabello y Sus Factores
 When Should I Be Concerned About Cramping During My Pregnancy?
When Should I Be Concerned About Cramping During My Pregnancy?
 Understanding the Growth of the Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Menstrual Health Supplements Market
Understanding the Growth of the Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Menstrual Health Supplements Market
 Premium Roofing Tile Solutions in Des Moines, IA by Joury Tile Service
Premium Roofing Tile Solutions in Des Moines, IA by Joury Tile Service
 How a Verified Gastroenterologist Email List Transformed a Healthcare Marketing Campaign
How a Verified Gastroenterologist Email List Transformed a Healthcare Marketing Campaign
 What Are the Main Compliance Areas Where AI Can Be Beneficial?
What Are the Main Compliance Areas Where AI Can Be Beneficial?







