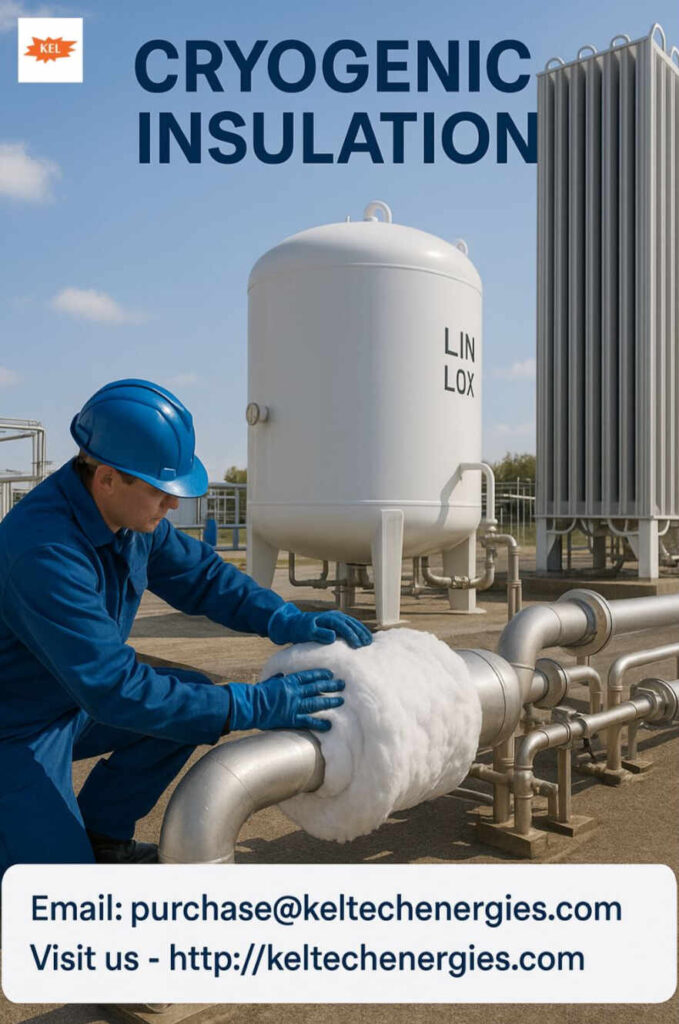
Cryogenic insulation is a specialized form of thermal insulation used in applications that involve extremely low temperatures, often below -150°C (-238°F). It plays a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency, safety, and performance of systems that store or transport liquefied gases such as liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, LNG (liquefied natural gas), and liquid helium. As industries like aerospace, healthcare, energy, and manufacturing continue to rely on cryogenic technology, the importance of effective cryogenic insulation has never been greater.
Understanding Cryogenic Insulation
Cryogenic insulation is designed to minimize heat transfer from the surrounding environment to materials stored at cryogenic temperatures. At such low temperatures, even a small amount of heat intrusion can lead to significant boil-off of the liquefied gases, causing loss of product and increased pressure within storage vessels. Proper insulation prevents this, improving efficiency and reducing operational risks.
Various cryogenic insulation materials are used depending on application needs, including:
- Vacuum Insulated Panels (VIPs): These are high-performance insulation systems that use a vacuum to minimize heat transfer.
- Foam Insulation (e.g., Polyurethane or Polyisocyanurate): Lightweight and cost-effective, foam insulation is often used in pipelines and storage tanks.
- Perlite and Aerogel: These materials offer excellent thermal performance and are widely used in the insulation of cryogenic vessels and pipelines.
- Multi-Layer Insulation (MLI): Commonly used in space applications, MLI consists of multiple layers of reflective foils separated by spacers to reduce radiant heat transfer.
Each of these materials is chosen based on the specific application requirements such as temperature range, mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and ease of installation.
Applications of Cryogenic Insulation
Cryogenic insulation finds application across numerous industries, such as:
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): Cryogenic insulation is vital in the LNG industry, where natural gas is cooled to approximately -162°C for storage and transport. Insulated storage tanks and pipelines ensure minimal loss during transit.
- Medical and Research Facilities: Laboratories and healthcare institutions rely on cryogenic insulation to safely preserve vaccines, biological samples, and sensitive reagents using liquid nitrogen.
- Aerospace Sector: Cryogenic insulation is essential in aerospace, where it ensures the stable storage and use of cryogenic fuels like liquid hydrogen and oxygen in rocket propulsion systems.
Cryogenic insulation ensures safe and efficient handling of these volatile substances.
- Food Processing and Storage: The food industry uses cryogenic techniques for flash freezing and transport of temperature-sensitive products. Effective insulation prevents contamination and maintains quality.
- Industrial Gases: Companies that manufacture and supply gases like argon, nitrogen, and helium rely on cryogenic insulation to transport and store these materials without loss.
Importance of High-Quality Cryogenic Insulation
High-quality cryogenic insulation brings several benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: Prevents sudden pressure buildup and explosions caused by rapid vaporization of cryogenic liquids.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy loss and maintains required temperature levels with minimal power usage.
- Cost Savings: Minimizes product loss due to evaporation and reduces the frequency of refilling cryogenic containers.
- Environmental Protection: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing fuel consumption in transportation and storage.
Challenges in Cryogenic Insulation
While cryogenic insulation offers many benefits, its implementation comes with specific challenges, including:
- Material Selection: Not all materials can withstand extreme cold without becoming brittle or losing integrity.
- Moisture Ingress: Water vapor can condense and freeze within insulation systems, causing damage and reducing efficiency.
- Mechanical Stress: Cryogenic systems often face expansion and contraction due to temperature fluctuations, demanding flexible and durable insulation materials.
- Installation Complexity: Proper installation is crucial, as even minor gaps can lead to thermal bridging and performance degradation.
Future Trends in Cryogenic Insulation
As global industries move towards cleaner energy and more advanced technologies, the future of cryogenic insulation looks promising:
- Hydrogen Economy: With the growing adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source, demand for cryogenic storage and transport solutions is expected to rise, driving innovation in insulation materials and designs.
- Advanced Materials: Research is underway to develop nanotechnology-based insulators and aerogels with superior thermal resistance and durability.
- Sustainability Focus: Eco-friendly and recyclable insulation materials are gaining traction as industries aim for sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Cryogenic insulation is a cornerstone of modern technological infrastructure, enabling the safe and efficient handling of materials at ultra-low temperatures. Whether it’s storing life-saving vaccines, transporting clean fuels, or launching satellites into space, cryogenic insulation ensures these processes run smoothly and safely. As the world continues to advance, investing in reliable and efficient cryogenic insulation will remain essential across multiple industries.
- Choosing the Right Cryogenic Insulation for Your Project
- Cryogenic Insulation refers to specialized thermal insulation materials and systems designed to maintain extremely low temperatures, typically below -150°C, used in applications involving liquefied gases like liquid nitrogen, oxygen, or LNG (liquefied natural gas).
- Cryogenic insulation, Cryogenic insulation services, Cryogenic insulation services
Related posts:
 Easy EMI Card: Your Go-To Solution for Easy Monthly Payments
Easy EMI Card: Your Go-To Solution for Easy Monthly Payments
 Fitness for Mental Clarity: Unlock Your Focus and Inner Strength with DG FIT MIND
Fitness for Mental Clarity: Unlock Your Focus and Inner Strength with DG FIT MIND
 Top Carrier Oil Suppliers in India for Bulk & Wholesale Buyers
Top Carrier Oil Suppliers in India for Bulk & Wholesale Buyers
 Atlas Pro ONTV : La Révolution de la Télévision par Internet
Atlas Pro ONTV : La Révolution de la Télévision par Internet
 Luxury or Budget? Finding the Right Heathrow Transfer for You
Luxury or Budget? Finding the Right Heathrow Transfer for You
 What Is Cold Rolled Stainless Steel Coil and Why Does It Matter?
What Is Cold Rolled Stainless Steel Coil and Why Does It Matter?
 Make Impact with Commercial Signs Raleigh NC: A Strategic Guide to Business Success
Make Impact with Commercial Signs Raleigh NC: A Strategic Guide to Business Success
 Essentials Hoodie Design Philosophy: Minimalism Meets Statement
Essentials Hoodie Design Philosophy: Minimalism Meets Statement